1. Introduction
RCube is routing software. It computes a route from an origin point pOr to a destination point pDest, starting at START_TIME, using GRIB weather files and the boat’s polar.
The algorithm is based on isochrones. Starting from pOr, RCube computes all points reachable within the time step T_STEP (isochrone 0). From each point on isochrone 0, it computes all points reachable within T_STEP again (isochrone 1), and so on, until pDest is reached (destination reached). If the weather time coverage is insufficient, the process stops (destination unreached).
RCube then proposes a route: either the optimal route from pOr to pDest, or the route from pOr to the point on the last isochrone that is closest to pDest.
GRIB (GRIdded Binary) files contain meteorological values on a latitude/longitude grid.
Routing mainly uses:
- 10 m wind,
- waves.
GRIB files with ocean currents can also be used by RCube.
The polar describes the boat’s speed as a function of true wind speed (TWS) and true wind angle relative to the boat’s axis (TWA).
Wave polars (if available) apply a multiplier to boat speed based on wave height and the wave angle relative to the boat. Typically, head seas reduce speed (e.g., 60%), whereas following seas increase it (e.g., 120%).
Additional parameters influence routing. You can define DAY_EFFICIENY and NIGHT_EFFICIENCY to reflect crew capability. For example, 80% means RCube uses 80% of the speed given by the boat polar (night efficiency is often lower than daytime).
Define a THRESHOLD below which sailing speed triggers engine use. Engine speed is set by MOTOR_S.
X_WIND multiplies wind speed. If, for example, you estimate that GRIB wind is 20% too low, set X_WIND to 1.2.
MAX_WIND sets a maximum wind speed. Routing favors paths that avoid winds above this value.
PENALTY0 is the time lost during a tack (seconds), PENALTY1 during a gybe (seconds), and PENALTY2 during a sail change (seconds).
When computing the next isochrone, RANGE_COG defines the span (−90° to +90°) relative to the direct course to the destination; COG_STEP defines the angular granularity (e.g., 5°).
2. Interface
Basemap
The route is displayed over a basemap: either Windy or OpenSeaMap.
Press <Ctrl S> to switch basemaps.
Note: switching resets the current route.
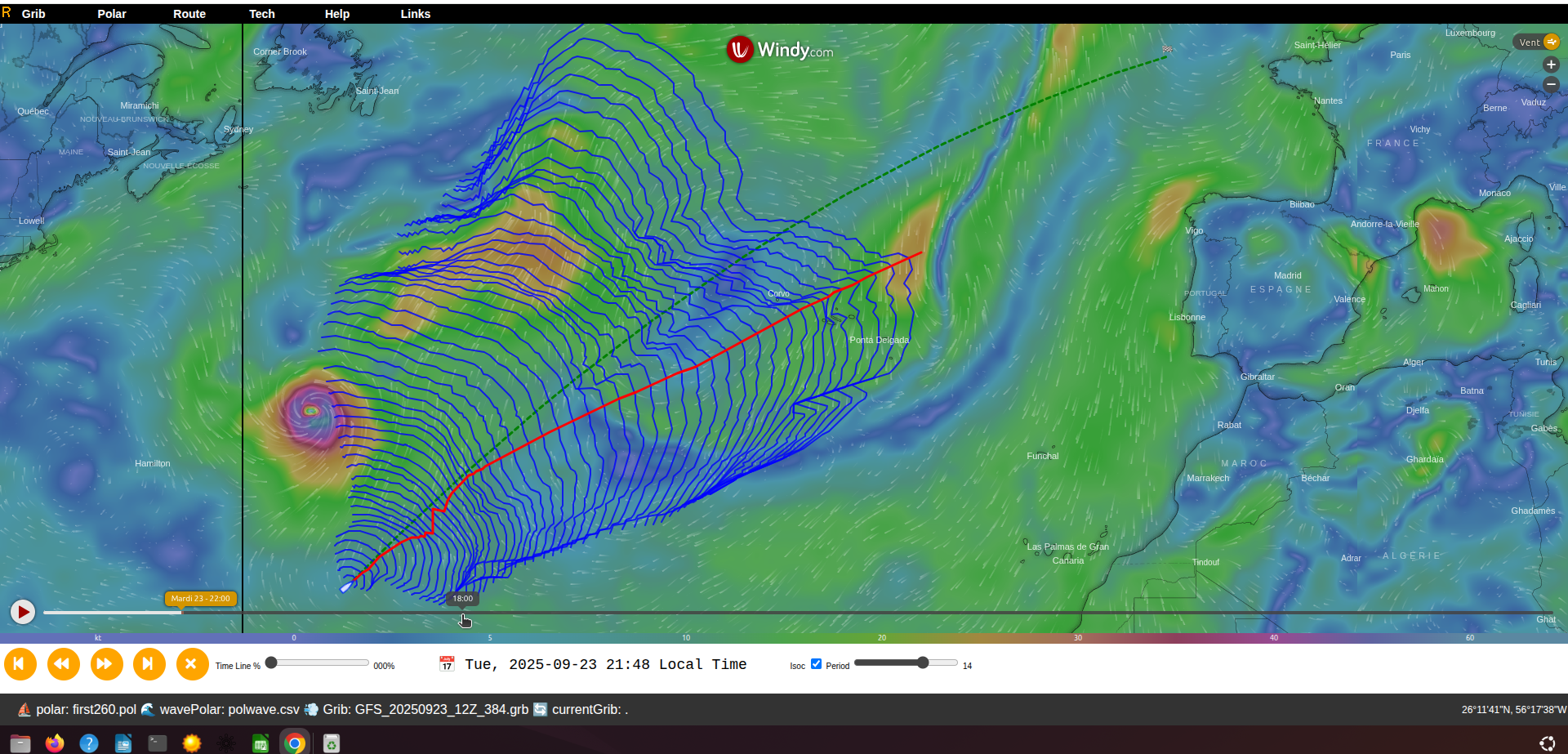
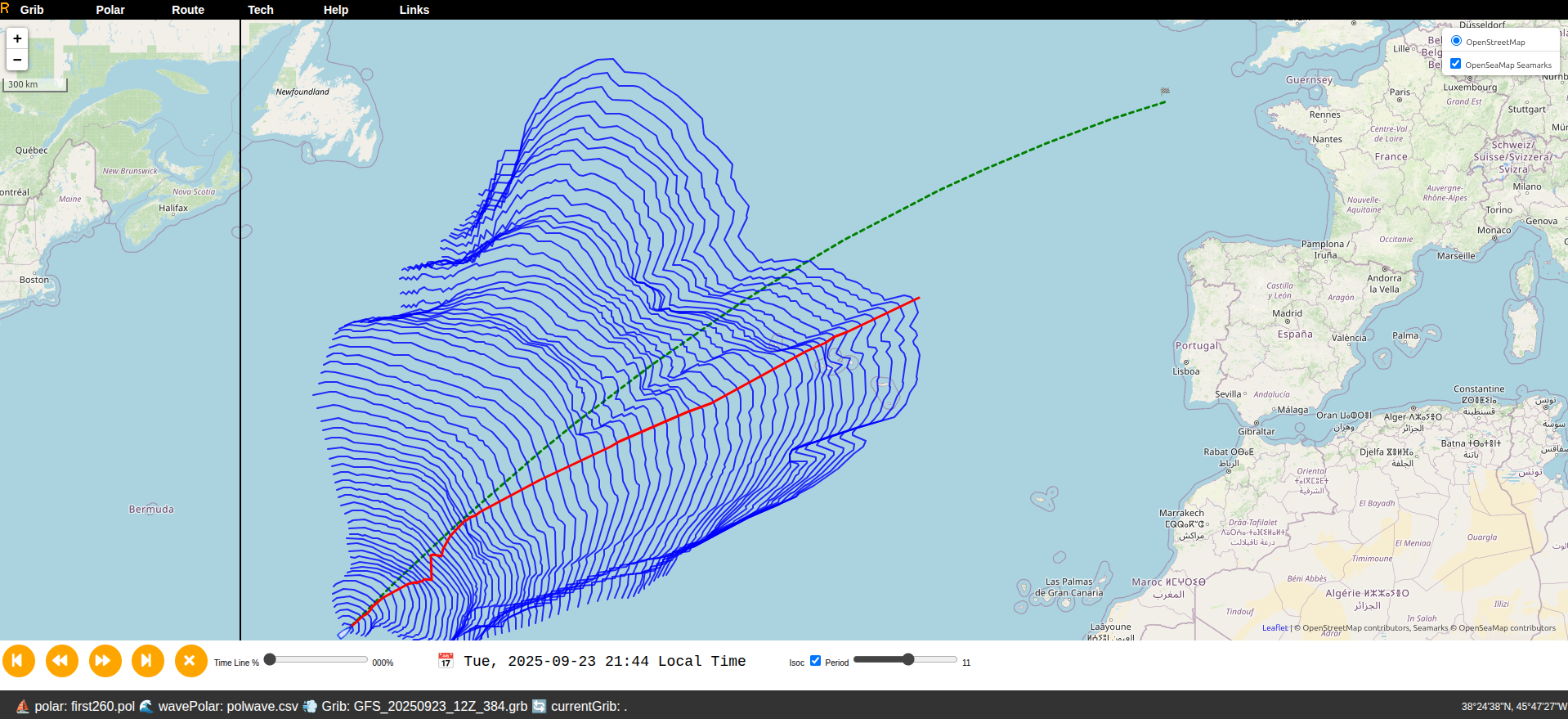
Screen Layout
Top bar
A menu bar provides access to:
- GRIB
- Polar
- Route
- Tech
- Help
- Links
- Sign In
Bottom bar
- If a route is available, a time bar with:
- play/pause controls and a route reset button,
- a time slider,
- local date and time,
- a button and slider to control isochrone display.
- A status bar with:
- on the left: the boat polar, wave polar (if any), wind GRIB, and current GRIB (if any),
- the latitude and longitude beneath the mouse pointer.
Center pane
- Windy, or
- OpenSeaMap.
With Windy, the Windy time slider appears at the bottom of the center pane.
Right-Click Menu
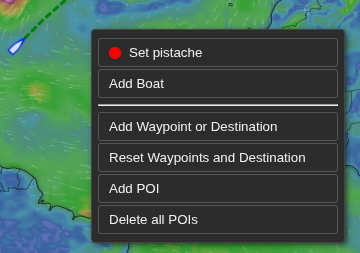
- Set the boat position (one line per boat with the boat’s color),
- Add a boat (see next figure),
- Add waypoints (by convention, the destination is the last waypoint),
- Erase all waypoints (and thus the destination),
- Add POIs (points of interest),
- Erase all POIs.

3. Menu Bar
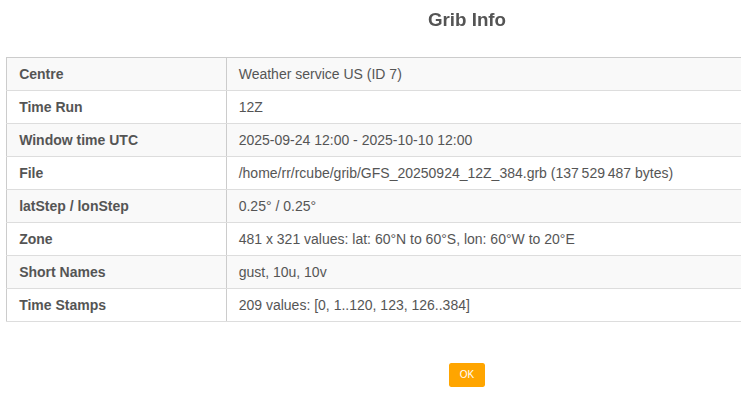
GRIB Menu
View the current GRIB description or choose another GRIB file.
GRIBs are mainly used for wind. GRIBs for currents are also supported.
Polar Menu
View and select the polar used for routing.
Both boat polars and wave polars are supported.
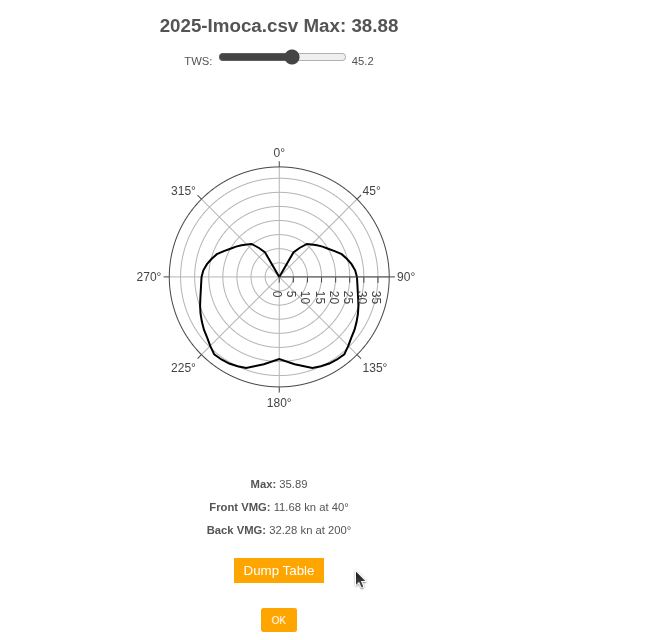
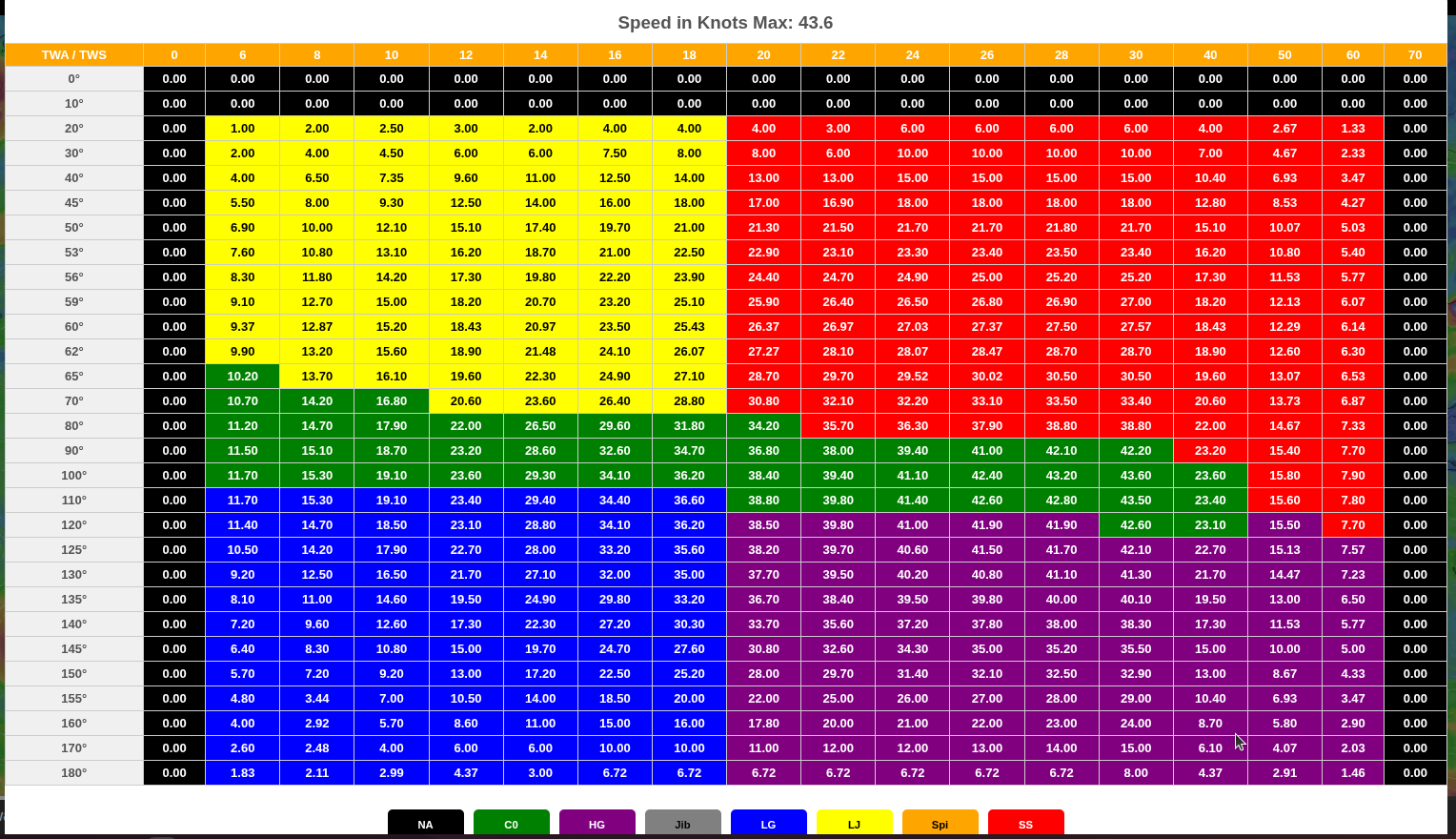
Route Menu
Use this menu to:
- launch a routing,
- retrieve the report for a previously computed routing,
- dump the last route,
- view the simulation report to search for the best departure time,
- compare different competitors.
Route » Launch
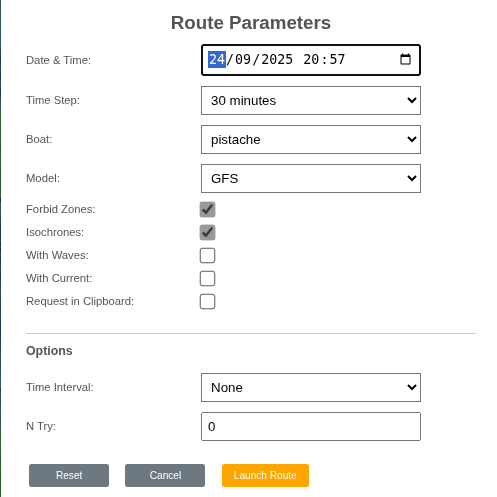
Start a routing at the desired date with the desired precision (time step).
- Date: departure date (local time),
- Time step: precision (e.g., 15 minutes),
- Boat: the selected boat, or all to benchmark several boats,
- Model: the weather model,
- Forbid Zones: when unchecked, ignore forbidden zones (land, etc.),
- Isochrones: show isochrones,
- With Waves: account for waves if a wave polar exists,
- With Current: account for currents if a current GRIB exists,
- Request in Clipboard: copy the server request to the clipboard (debugging).
To compute the best departure time, set:
- Time Interval: time between attempts,
- N Try: number of attempts.
After computation, RCube generates a report. As long as the route isn’t deleted, you can reopen it later from Route Report.
Route » Report
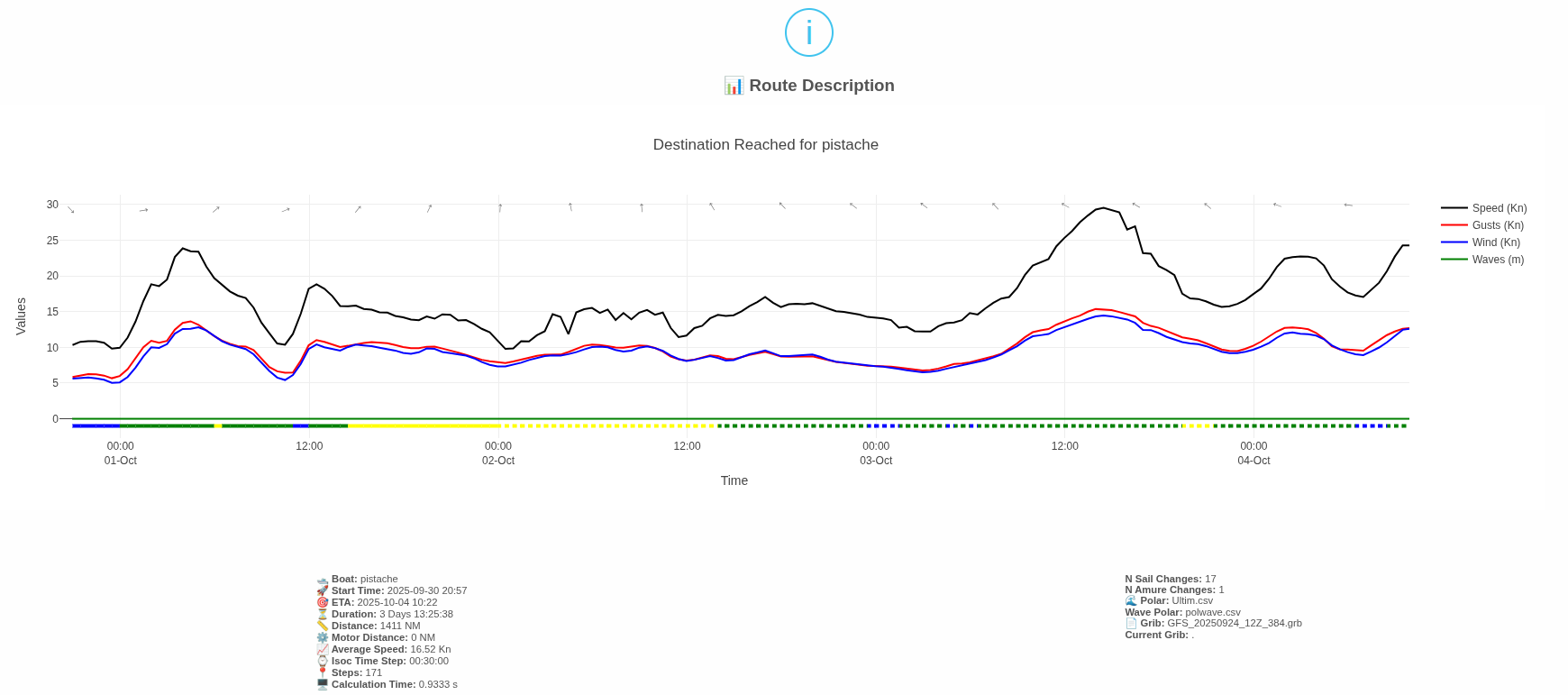
This report summarizes the route (departure, ETA, duration, etc.). It also shows time series from departure to arrival for:
- wind direction, wind speed, and gusts (if available) at the boat’s position,
- boat speed,
- wave height (if available).
Below the time axis, a colored band indicates the sail in use (if available). Dotted vs. solid lines distinguish the tack (starboard vs. port).
Route » Dump
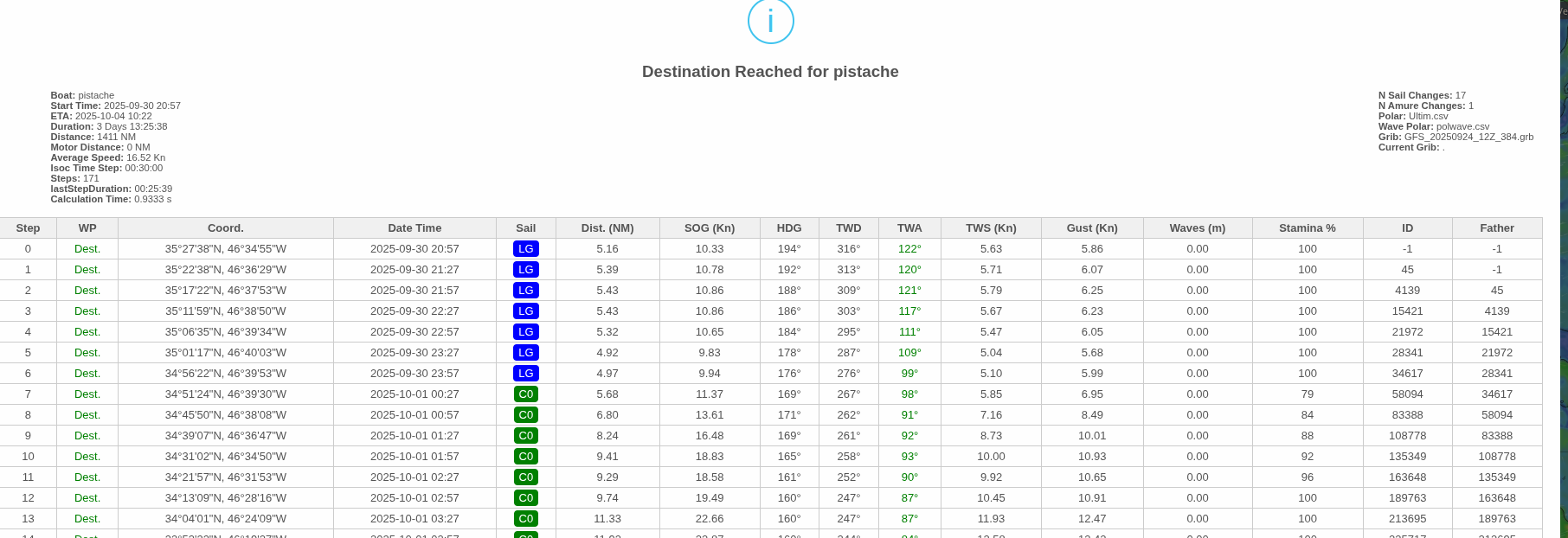
The complete route with all available data. Each row corresponds to a timestamp (the associated isochrone).
Best Time Report
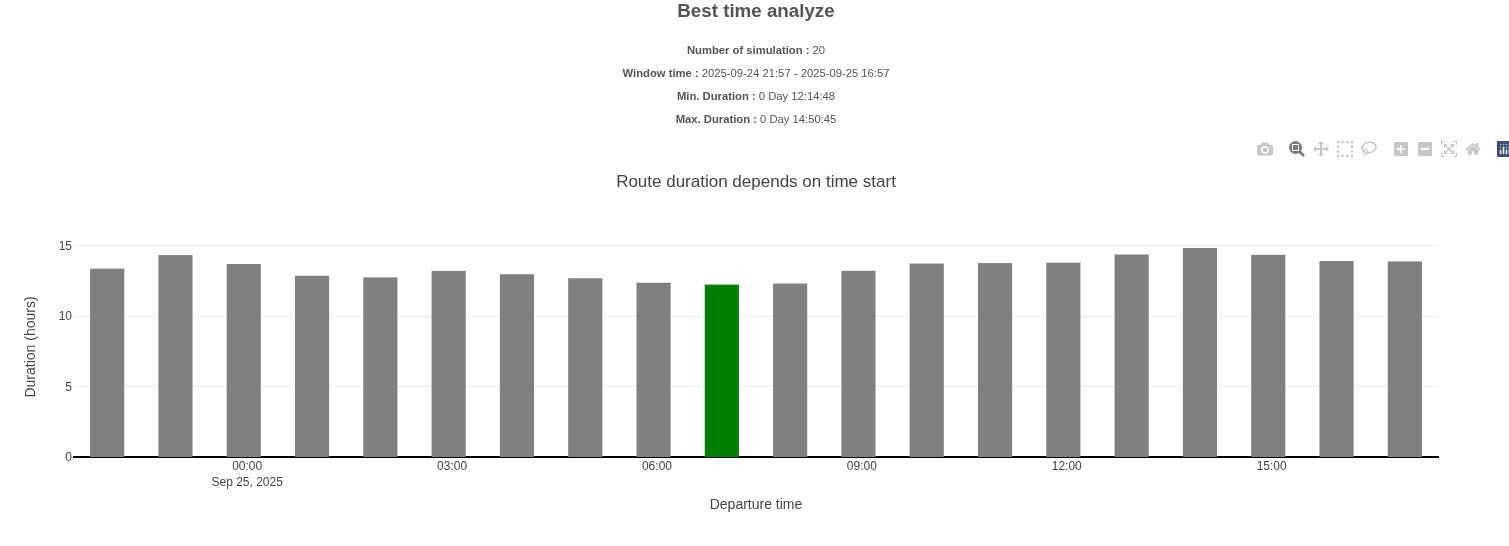
A chart showing, for each selected departure time, the route duration. The green bar marks the departure time with the minimum duration.
Benchmark Report
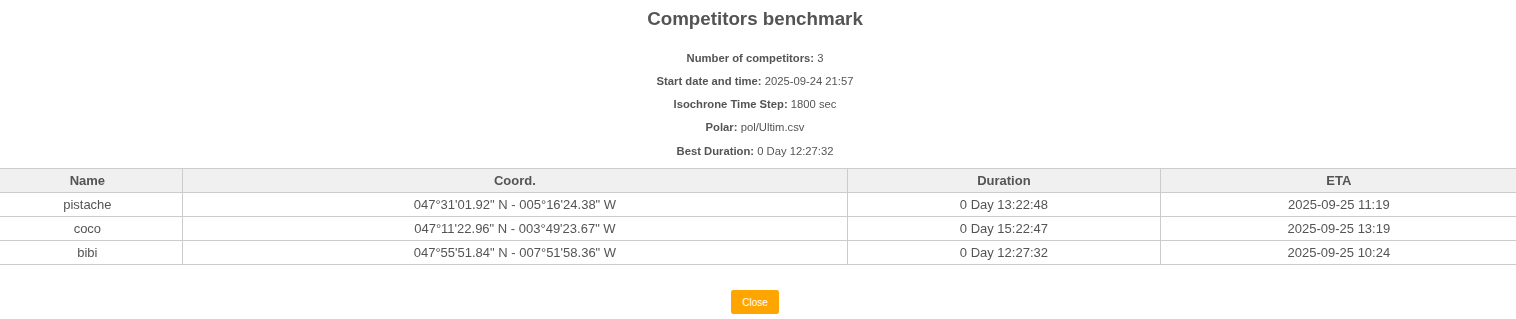
A table comparing competitor performance (one row per competitor).
Tech Menu
This menu has four submenus:
- Waypoints
- Change
- Manage Competitors
- Stamina
Waypoint Distances
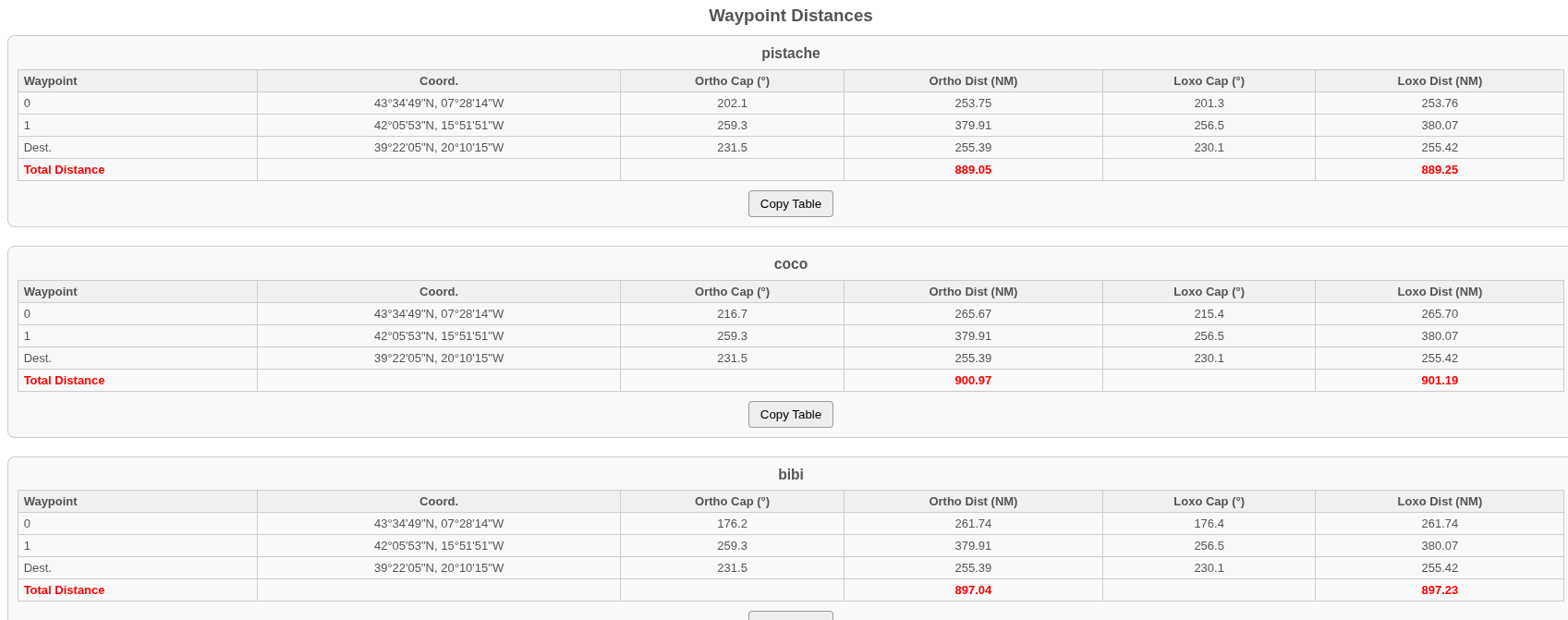
One table per competitor shows: distance and bearing from the competitor to the next waypoint, and distance and bearing from waypoint to waypoint up to the destination.
Distances and bearings are provided as rhumb-line (loxodromic) and great-circle (orthodromic).
Change
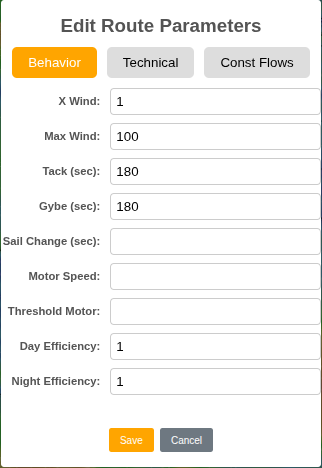
This section describes only the Behavior tab (other tabs are developer-only).
- X Wind: multiplier applied to wind speed (GRIB winds are often underestimated; e.g., use 1.15),
- Max Wind: maximum wind to avoid overly windy areas,
- Tack: time lost during a tack (s),
- Gybe: time lost during a gybe (s),
- Sail Change: time lost during a sail change (s),
- Motor Speed: engine speed (kt),
- Threshold Motor: sailing speed below which the engine engages,
- Day Efficiency: daytime crew efficiency (typically 100%),
- Night Efficiency: nighttime crew efficiency (e.g., 90%).
Manage Competitors
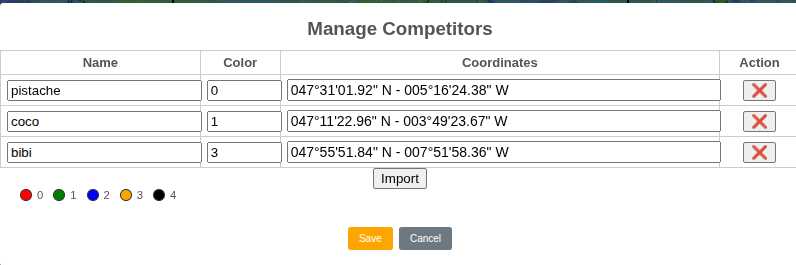
A table with one row per competitor lets you edit a competitor’s name, color, and geographic coordinates. You can also delete competitors.
To add a competitor, use the right-click menu.
The Import button imports competitors from a CSV file compatible with the I.T.Y.C Dashboard module used for Virtual Regatta.
Stamina
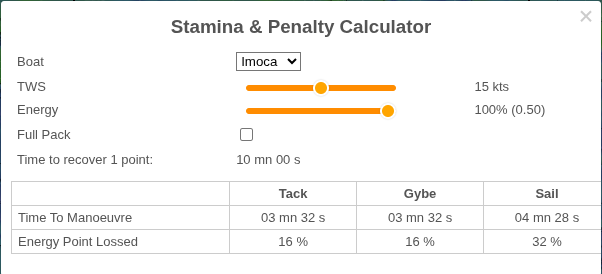
A Stamina & Penalty calculator. Useful for Virtual Regatta players.
Based on your inputs (boat type, wind speed, skipper energy, and whether you have the “full pack”), it estimates:
- time to recover 1 energy point,
- maneuver times (tack, gybe, sail change),
- energy lost per maneuver.
Help Menu
Provides options to:
- show Help,
- show About,
- send Feedback.
Links Menu
Links to various map and weather sites are offered, based on the main boat’s geographic area.
Sign In Menu
Sign in to gain elevated privileges.
Appendix
Glossary (mini)
- Basemap
- The background map layer (Windy or OpenSeaMap) on which RCube overlays routes, markers, and layers.
- GRIB
- GRIdded Binary meteorological data used by RCube (wind, waves, currents) on a latitude/longitude grid.
- Polar (boat polar)
- A table/curve of boat speed versus true wind speed (TWS) and true wind angle (TWA).
- Wave polar
- A multiplier applied to boat speed as a function of wave height and wave angle relative to the boat.
- Isochrone
- The set of points reachable after a fixed time step. RCube builds successive isochrones to find a route.
- Time step
- The time interval (Δt) between successive isochrones and samples. Smaller steps increase precision and computation time.
- Waypoint (WP)
- An intermediate target. By convention, the last waypoint is the destination (pDest).
- POI
- Point of interest shown on the map. POIs are informational and are not used by the router.
- Model (weather model)
- The numerical weather dataset used to populate GRIB variables for routing.
- Benchmark
- A comparison of competitors or boats over the same route to evaluate relative performance.